Parkinson\'s Disease Umn Or Lmn
These disorders are characterized by the degeneration of motor neurons in the cerebral cortex spinal cord brain stem and pyramidal tracts. Motor neuron disease can affect either upper motor neurons UMNs or lower motor neurons LMNs.

Pyramidal Vs Extrapyramidal Extrapyramidal And Movement Disorders Nursing Books Disorders
This specifically involves the glossopharyngeal nerve IX vagus nerve X and hypoglossal nerve XII Both UMN and LMN are affected.

Parkinson\'s disease umn or lmn. WEAKNESS LOSS OF VOLUNTARY MOVEMENT - muscle cannot exert normal force most important clinical feature of motoneuron UMN LMN disorders. Muscle tone and reflex. Driven to Develop New Strategies By better understanding the changes in brain circuitry that occur in Parkinsons we will develop new treatment strategies to improve the lives of patients.
Evidence of shared genetic susceptibility. It is a neurodegenerative disease of unknown etiology characterized by both UMN and LMN lesions. - UMN disease manifests as spasticity slowed movements poor dexterity pseudobulbar affect hyperreflexia and pathologic reflexes.
Delays the need for gastrostomy feeding and ventilatory support. Mechanism not really understood. Examination of dogs with UMN spinal cord disease often reveals increased tone because there is resistance to flexion of the stifle.
Lesions were classified as LMN UMN or mixed on the basis of the presence or absence of 1 the bulbocavernosus reflex 2 lower limb deep tendon reflexes below the neurologic level of injury and 3 the Babinski sign. Motor neuron disease describes a collection of clinical disorders characterized by progressive muscle weakness and the degeneration of the motor neuron on electrophysiological testing. Upper Motor Neuron.
The LMN phenotype of MND progressive muscular atrophy PMA is characterised by progressive LMN signs without clinical evidence of UMN dysfunction although a significant proportion develop UMN signs during the disease course28 It is estimated that the syndrome represents 5 of MND cases and may be characterised by slower progression than other forms of MND28 In the absence of UMN signs confident differentiation from other LMN. The UMN system modulates or controls the TGLM and therefore controls muscle tone and reflex. Respiratory muscle involvement entails alveolar hypoventilation decreased cough capacity and the risk of aspiration due to bulbar dysfunction.
Disease of the UMN lesion can cause increased tone and reflex. Eventually patients lose all voluntary muscular control. A progressive degenerative disorder characterized by abnormal motor movement due to lack of dopamine Is Parkinsons Disease LMN or UMN.
The use of respiratory muscle aids noninvasive mechanical ventilation and manually and mechanically assisted cough can improve survival quality of life and avoid hospitalization when. UMN disease should have distinctly different signs from LMN disease Cervical spinal cord disease and diffuse LMN disease can sometimes be confused without thorough examination Diseases that affect the neuromuscular system can look very similar Gait evaluation is probably the most important aspect of the exam Acute localization is key. Cognitive impairment is generally spared.
It often presents in the 5th6th decade of life with fasciculations of the hands and bulbar muscles and progresses to spastic weakness of the extremities bulbar weakness and dysphagia. PARKINSONS DISEASE Parkinsons Disease is an extrapyramidal motor system disorderin which specific neurons in the extrapyramidal motor system degenerate resulting in the inability to modulate movement appropriately NUCLEI OF THE EXTRAPYRAMIDAL MOTOR SYSTEM Nuclei of the Extrapyramidal Motor System. As discussed above the term motor neuron disease has varying meanings in different countries.
It has long been recognized that signs of motor neuron disease MND may accompany clinical evidence of parkinsonism in different neurodegenerative conditions. B senso lato all neurons forming descending tracts that ultimately play on LMN tr. Lesion affects nerves or their acxons at or below the level of the brainstem usually in the final common pathway.
PARESIS reduced voluntary movement. Driven to Train the Next Generation of Leaders in PD Research The UMN Udall Center is poised to promote coordinate and implement the academic mission of training the next generation of leaders in PD research both within the Center and across the UMN. Muscular twitch caused by random discharge of a LMN and its muscle fibers LMN Disease.
Conditions that exhibit both UMN and LMN signs. In Parkinsons disease the upper motor neuron is indirectly affected. It tends to prolong muscle function but does not have any effect on the decline in muscle strength.
Lesion found in the descending motor tracts withing the cerebral motor cortex internal capsule brainstem or spinal cord. This stiffness can also manifest in the protraction phase of the gait and appear as swinging out of. The incidence and etiology of LMN vs UMN lesions were determined for the following neurologic levels.
Familial aggregation of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis dementia and Parkinsons disease. Most effective in disease that presents with bulbar signs. By using the Columbia University Division of Movement Disorders database we reviewed data from 5500 cases of parkinsonism and recorded the presence of upper motor neuron UMN dysfunction lower motor neuron LMN.
Motor neuron disease MND is a family of progressive neurodegenerative diseases characterized by loss of upper motor neurons UMN in the motor cortex andor lower motor neurons LMN in the brainstem and spinal cord. What is Parkinsons disease. PBP is a disease that attacks the nerves supplying the bulbar muscles.
It is thought thatby blocking sodium channels the effect of glutamate is greatly.

Parkinson S Disease Bradykinesia Tremor Rigidity Postural Reflect Impairment Destruction Of Dopaminergic Neurons In The Pars Compacta Of The Substantia Ppt Download
Modifiable Risk Protective Factors For Parkinson S Disease Investigated Download Scientific Diagram

Neurology Part 2 Phase 2 Kaveesha Rajapaksa Ryad

Umn V Lmn Speech Disorder Speech And Language Language Therapy

Neurology Part 2 Phase 2 Kaveesha Rajapaksa Ryad

Pathophysiology Of Nervous System Diseases Mehtap Kaar Koak

Upper Motor Vs Lower Motor Neuron Disease How To Relief Motor Neuron Disease Treatment Motor Neuron Neurons

Neurology Part 2 Phase 2 Kaveesha Rajapaksa Ryad

Neurology Part 2 Phase 2 Kaveesha Rajapaksa Ryad

Disorders Of The Motor System Jeanette J Norden

Picture Parkinsons Disease Parkinsons Homeopathy
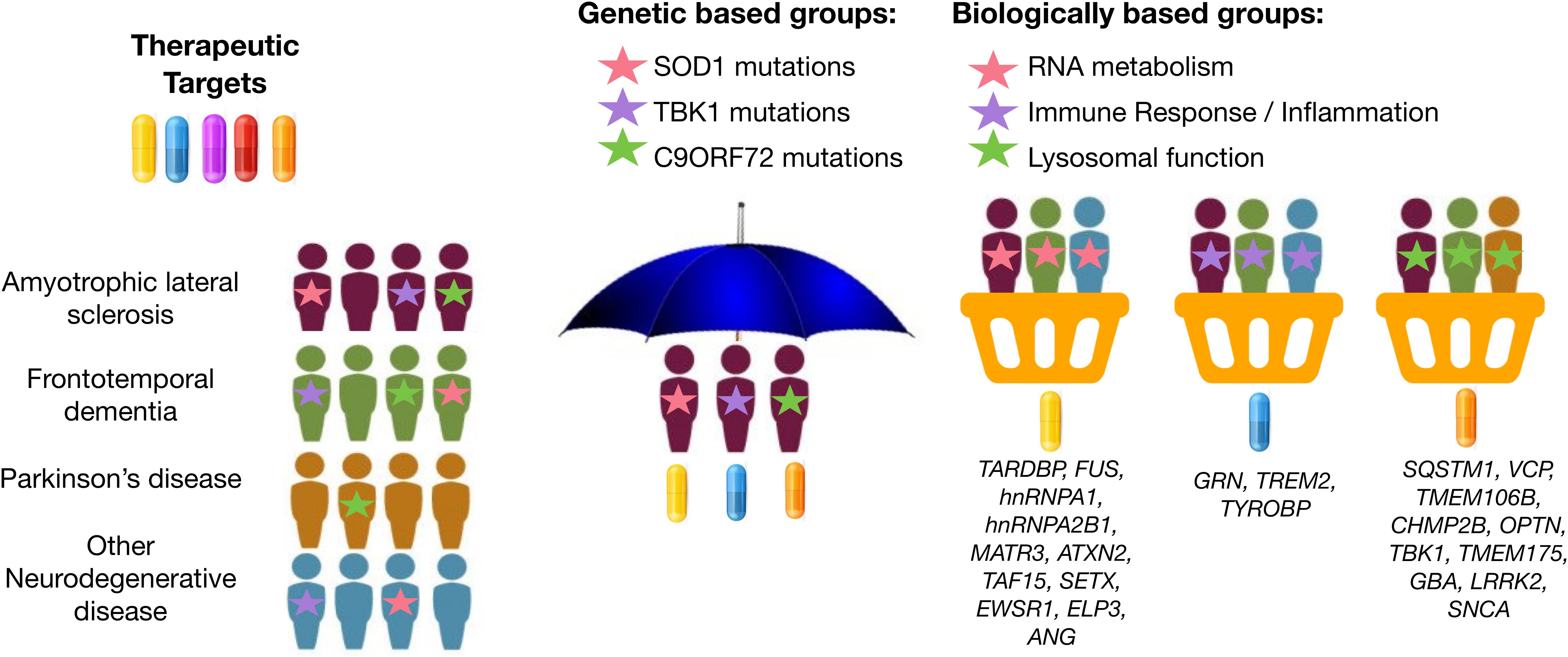
Frontiers Moving Toward Patient Tailored Treatment In Als And Ftd The Potential Of Genomic Assessment As A Tool For Biological Discovery And Trial Recruitment Neuroscience

Modifiable Risk Protective Factors For Parkinson S Disease Investigated Download Scientific Diagram

Modifiable Risk Protective Factors For Development Of Parkinson S Disease Download Scientific Diagram
The Role Of Upper And Lower Motor Neurons In Different Als Variants Download Scientific Diagram

Parkinson S Disease Mnemonic Quick Study Technique The Beat Yt Parkinsonism Youtube

Upper Motor Neuron Vs Lower Motor Neuron Medik Ukm Motor Neuron Physical Therapy School Neurons

Parkinson S Disease Foundation Resource List 11 By Sharon Klein Issuu
Post a Comment for "Parkinson\'s Disease Umn Or Lmn"